Medication: Muscle relaxants and anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDS, diazepam, baclofen (should be taken under the prescription of doctor).
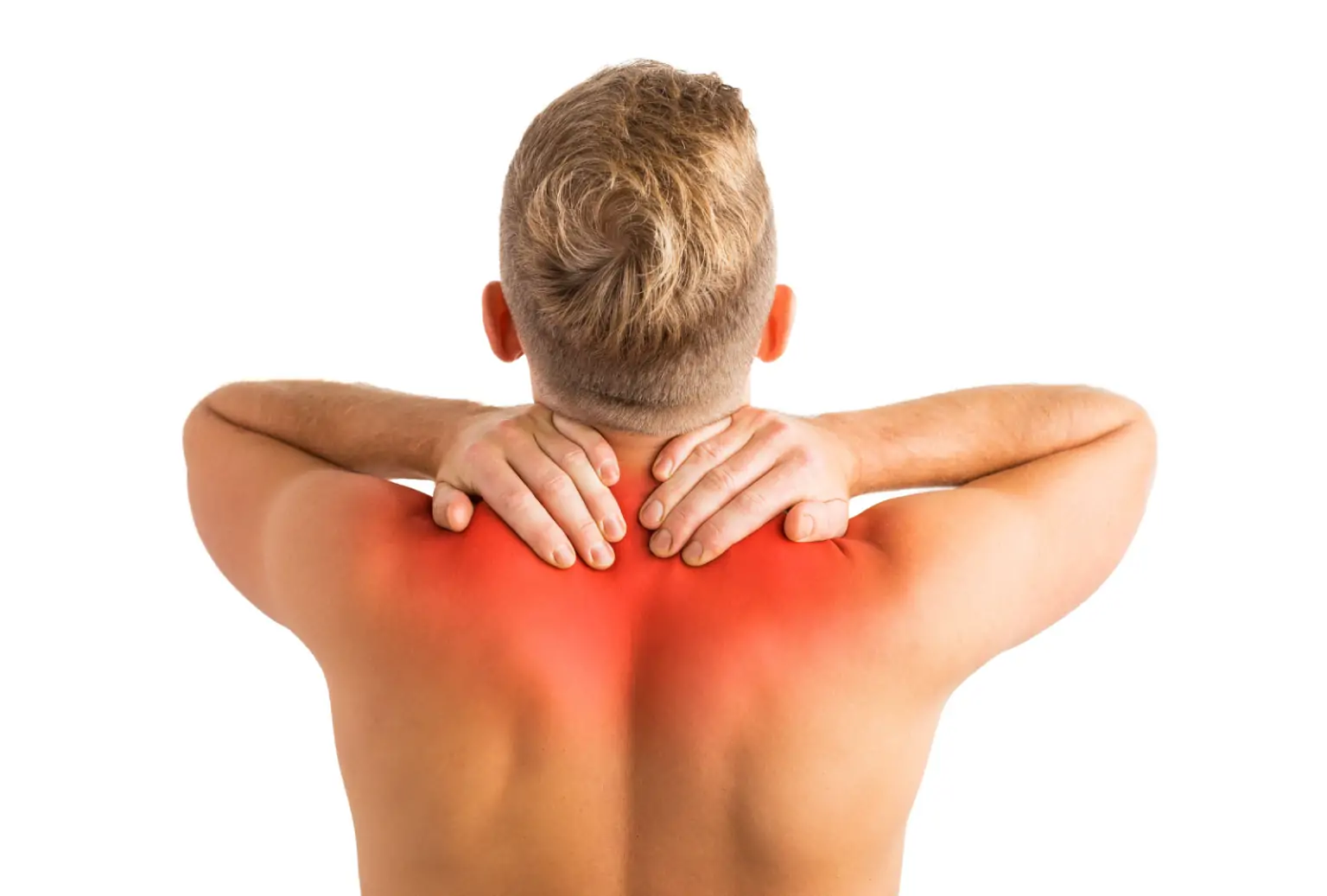
Physiotherapy treatment: The physiotherapist uses different methods of treatment to treat the symptoms of muscle spasms.
Cryotherapy: Utilize cryotherapy by applying ice packs, cool baths, cooling garments, cold towels, etc. help to control spasms.
Thermotherapy: Thermotherapy application by hot packs, warm swimming, etc. relaxes the muscles.
Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS): Transcutaneous electrical stimulation reduces muscle spasm and pain thus restoring muscle function.
Relaxation: Body relaxation combined with deep breathing enhances the effect of treatment techniques used. Relaxation and re-education about the breathing patterns help to decrease the tension in the muscle and provides pain relief.
Massage: Massaging the area with a massager or can also be done manually by using techniques like deep tissue massage, gently rubbing the muscle, and pinching or stroking massage produces relaxation, thus increasing the range of motion and also causes stretching effect. Massaging the affected muscle may decrease the spasm and thus reduces pain.
Stretching: Stretching helps to release the spasmed muscle stuck for long periods in a shortened state. Over some time these muscles can cause pain, daily stretching of these muscles can relieve pain.
Joint manipulation: Joint manipulation uses gentle movements to stimulate the joint movement by reducing the muscle spasm and pain.
Strengthening: Strengthening exercises play a major role in decreasing muscle spasms. Due to spasms, the muscle is not often used, thus making these muscles weaker over time. Strengthening exercises helps these muscles to regain strength and mobility.
Mild exercises: Mild exercises should be done to maintain strength and mobility. These may include
- Static cycling
- Mild staircase climbing
- Jogging
- Swimming