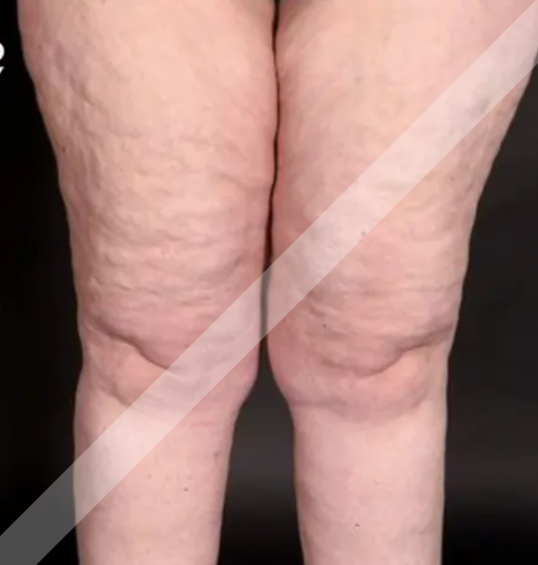
What is Lipedema?
Lipedema is a chronic, progressive disorder of fat metabolism that primarily affects women and is characterized by a symmetrical and disproportionate accumulation of fat, typically in the lower limbs (hips, thighs, buttocks, and legs) and sometimes in the arms. This fat distribution usually spares the hands and feet and is often associated with pain, tenderness, easy bruising, and swelling that does not respond to diet or exercise. The condition is believed to have a hormonal and genetic component and is often misdiagnosed as simple obesity or lymphedema.
It may worsen over time and can significantly impact mobility and quality of life if not properly managed.
Treatment Of Lipedema
Medications: Ibuprofen, naproxen, paracetamol, pregabalin, gabapentin, etc
Note: Medication should not be taken without the doctor’s prescription.
Physiotherapy Treatment Of Lipedema
Physiotherapy plays a key role in the conservative management of lipedema. While it cannot eliminate the abnormal fat deposits, it helps manage pain, swelling, reduced mobility, and fatigue, and improves functional ability and quality of life.
- TENS: TENS is used to reduce pain, by stimulating the release of endorphins.
- Interferential Therapy (IFC): IFC stimulates deeper tissues, reducing pain and inflammation.
- Therapeutic Ultrasound: Therapeutic Ultrasound helps to generate heat and promote tissue healing.
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD):
- A gentle, rhythmic massage to stimulate the lymphatic system
- Reduces fluid retention, pain, and tightness
- Usually done 2–5 sessions/week depending on stage
- Can be taught to the patient for self-MLD
- Compression Therapy:
Use of medical-grade compression garments (stockings, sleeves)
Prevents fluid buildup, supports tissues, reduces discomfort
- Exercise Therapy:
- Low-Impact Cardiovascular Exercise
To stimulate lymphatic flow and improve circulation:
- Aquatic therapy (swimming, walking in water)
- Cycling (stationary or regular)
- Brisk walking
- Rebounding (mini trampoline) – if tolerated
- Resistance Training
- Builds muscle tone and improves function
- Focus on lower limbs and core
- Use light weights or resistance bands
- Stretching and Mobility
- Gentle stretching of calves, hamstrings, and hips
- Improves flexibility and reduces stiffness
- Lymphatic Taping (Kinesio Taping)
- Special taping technique used to:
- Support lymph drainage
- Reduce pain and heaviness
- Improve movement awareness
- Education & Self-Management Training
- Posture correction and body mechanics
- Importance of regular movement, especially in sedentary jobs
- Skin care to prevent infections (like cellulitis)
- Teaching self-MLD and home exercises
- Encouraging consistent use of compression garments
- Psychological and Behavioral Support
- Physiotherapists can help identify:
- Anxiety, low mood, or body image distress
- Refer to psychological or support services
- Encourage group exercise or support group participation