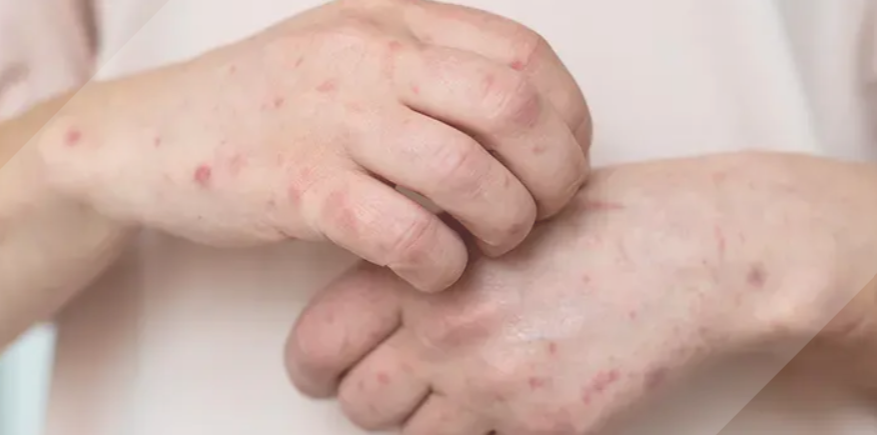
What is Leprosy?
Leprosy or Hansen's disease is a chronic infection that affects the mucous membrane, skin, and nerves. It causes discoloration, lumps, disfigurement, and deformities in the skin. Leprosy is spread when a healthy person comes in regular and close contact with the droplets of leprosy patients. The disease is most prevalent through respiratory route transmission and insects.
Types of Leprosy:
Intermediate Leprosy: Intermediate leprosy is the earliest stage of leprosy, patients suffer from flat lesions which may heal by themselves.
Tuberculoid Leprosy: Tuberculoid leprosy is a mild and less serious type of leprosy. People suffering from this disease have no sensation in the affected area, and some patches of flat and pale-colored skin. This infection heals on its own or may persist and progress to a more severe form.
Borderline tuberculoid Leprosy: Borderline tuberculoid Leprosy has symptoms similar to the tuberculoid but the infections may be smaller and more in number which may continue and revert to tuberculoid, or any other advanced form.
Mid-borderline Leprosy: The sign and symptoms of mid-borderline are similar to borderline tuberculoid leprosy. The symptoms include reddish plaques with numbness which may regress or progress to another form.
Borderline Leprosy: Borderline leprosy is a cutaneous skin condition, characterized by multiple wounds or scars, plaques, and flat raised bumps that may continue or regress.
Lepromatous Leprosy: Lepromatous Leprosy is a more severe type of disease with many lesions with bacteria. The affected region has numbness, and muscle weakness, full of bumps and rashes. Other symptoms include hair loss, limb weakness, and other body parts like the male reproductive system, kidneys, and nose are also affected.
Causes of Leprosy
Leprosy is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium Leprae, the causes of leprosy can be:
- Runs in families.
- Individuals with weakened immune systems.
- People living in high-risk areas.
- Close contact with the infected person.
- Malnutrition, etc.
Diagnosis Of Leprosy
Physical examination: A physical examination is done to look for the signs and symptoms of leprosy.
Biopsy: A biopsy is done by removing a small piece of skin or nerve and sent to the laboratory for testing.
Skin test: A skin test or a skin lesion biopsy is advised to determine the form of leprosy. A small amount of Hansen's disease-causing bacterium, which has been inactivated, is injected into the skin, typically on the upper forearm. Patients who have tuberculoid or borderline tuberculoid Hansen's disease will experience a positive result at the injection site.
Treatment Of Leprosy
Medications: Dapsone, Ofloxacin. Clofazimine, etc.
Note: Medication should not be taken without the doctor’s prescription.
Surgery: Surgery is indicated when the symptoms are not controlled by medication.
Physiotherapy Treatment Of Leprosy
Thermotherapy: Heat therapy enhances joint movement. The affected part is soaked in warm water, which also increases blood circulation.
Range of motion Exercises: Range of motion exercises can help maintain muscle bulk and tone. The physiotherapist suggests passive exercises followed by active assisted and then active exercises.
Bohler Iron: It can be used in the walking cast to prevent pressure on the calf area and for transmitting weight on the foot. Bohler iron enhances the healing process in case of ulcers.
Boots: The boot is a cast used to heal plantar ulcers on the forefoot. The cast is applied below the malleoli, covers the entire foot, just like a boot.
Assistive devices: Assistive devices can be recommended to protect the affected area from pressure injuries.
Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening exercises include resistive exercises which help increase muscle strength.
Skin Cleansing: Cleaning the skin by soaking the part in soap water, rubbing off thick skin, oiling, self-massage, and protecting the part from infection.
Splinting: Splints are used to immobilize the affected part. Static splints immobilize and prevent movement in the area, dynamic splints allow movements that help in maintaining function.
Elevation: The affected part is elevated to decrease inflammation by draining it.
Motor Training:Motor training is recommended for leprosy patients suffering from motor impairments such as grasp, pinch, and prehension to enable and enhance performance in ADL and work-related activities.
Patient Education
Not all exercises are suitable such as abrupt stops, starts, and changes in direction can put a fusion that is still healing at risk. Jogging or running, sports like basketball or football should be undertaken until a patient has been approved by the surgeon. If there is any shortness of breath, chest pain, or dizziness, then the activity should be immediately stopped.


